Basic knowledge on heat transfer |
Report |
|
Please tick the correct answers: | |
|
Convection and conduction are both processes of heat transfer. Existing common features have to be distinguished from differences. Which statements are true? | A fluid at rest should be considered the same as a heat-conducting solid body in terms of heat transport. Boundary layers cannot be meaningfully considered. |
Heat transfer in fluids always means convection. | |
Convection also always means heat conduction. | |
Heat conduction within a body is also know as internal convection. | |
Convection disrupts the normal heat conduction in the fluid and in extreme cases can mean a deterioration of heat transport. | |
|
In convective processes, heat is dissipated through fluid
layers. | A flue makes it possible to enhance convection. Since the process is still free of technical devices, this type of convection is still classed as free convection. |
In convection a distinction is made between temperature boundary layer and velocity boundary layer. | |
In convection heat is dissipated with the fluid flow. | |
|
A lot of heat transfer applications make use of the concept of convection. Which statements are correct? | The advantage of the freezer is that cold air sinks. This forms temperature layering. An exchange with uncooled air can only occur from the outside. This makes the freezer favourable in terms of energy use. |
Foamed substances have gas cavities. They are primarily suitable as insulating material, because the thermal conductivity of gases is low and convection in foam is practically non-existent. | |
The cooling capacity of a chiller is often increased by a fan. The increased air flow makes the heat transfer to the air more effective. | |
|
The following images show temperature and velocity profiles of a fluid at the flat wall. Which statements are true? | |
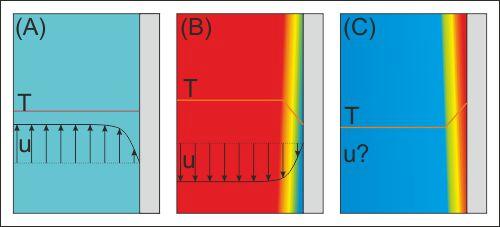 | Alpha (B) < Alpha (A) |
No convection occurs in (A). | |
The representation in (C) is enough to exclude pure heat conduction. | |
The representation in (B) is enough to exclude free convection. | |